# Contributing to OpenMMLab
Welcome to the MMYOLO community, we are committed to building a cutting-edge computer vision foundational library, and all kinds of contributions are welcomed, including but not limited to
**Fix bug**
You can directly post a Pull Request to fix typos in code or documents
The steps to fix the bug of code implementation are as follows.
1. If the modification involves significant changes, you should create an issue first and describe the error information and how to trigger the bug. Other developers will discuss it with you and propose a proper solution.
2. Posting a pull request after fixing the bug and adding the corresponding unit test.
**New Feature or Enhancement**
1. If the modification involves significant changes, you should create an issue to discuss with our developers to propose a proper design.
2. Post a Pull Request after implementing the new feature or enhancement and add the corresponding unit test.
**Document**
You can directly post a pull request to fix documents. If you want to add a document, you should first create an issue to check if it is reasonable.
## Preparation
The commands for processing pull requests are implemented using Git, and this chapter details `Git Configuration` and `associated GitHub`.
### 1. Git Configuration
First, make sure you have Git installed on your computer. For Linux systems and macOS systems, Git is generally installed by default. If it is not installed, it can be downloaded at [Git-Downloads](https://git-scm.com/downloads).
```shell
# view the Git version
git --version
```
Second, check your `Git Config`
```shell
# view the Git config
git config --global --list
```
If `user.name` and `user.email` are empty, run the command.
```shell
git config --global user.name "Change your username here"
git config --global user.email "Change your useremail here"
```
Finally, run the command in `git bash` or `terminal` to generate the key file. After the generation is successful, a `.ssh` file will appear in the user directory, and `id_rsa.pub` is the public key file.
```shell
# useremail is GitHub's email address
ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "useremail"
```
### 2. Associated GitHub
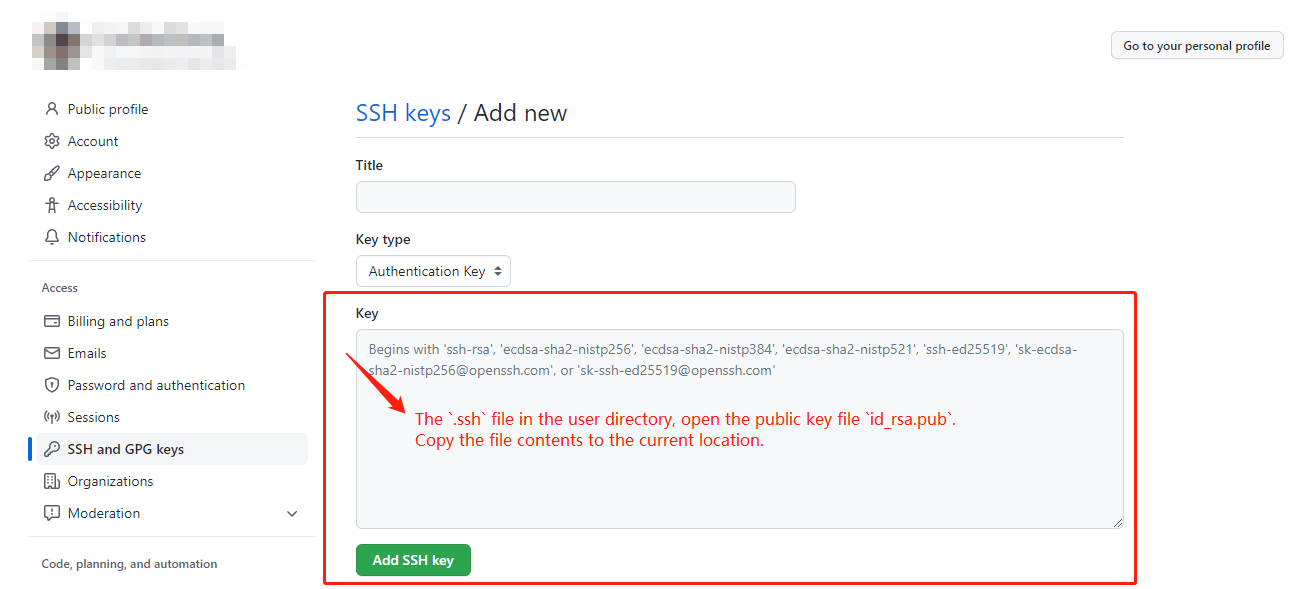
First, open `id_rsa.pub` and copy the entire contents.
Second, log in to your GitHub account to set it up.
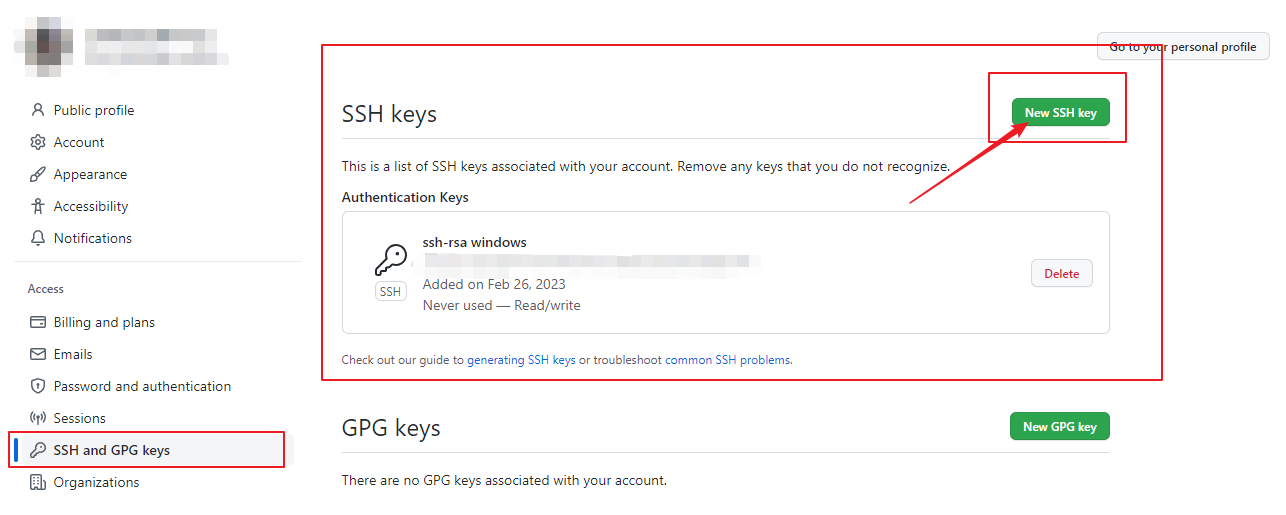 Click `New SSH key` to add a new SSH keys, and paste the copied content into Key.
Click `New SSH key` to add a new SSH keys, and paste the copied content into Key.
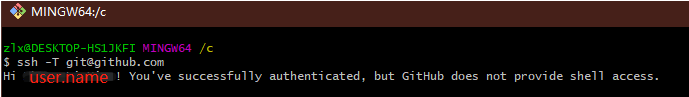
 Finally, verify that SSH matches the GitHub account by running the command in `git bash` or `terminal`. If it matches, enter `yes` to succeed.
```shell
ssh -T git@github.com
```
Finally, verify that SSH matches the GitHub account by running the command in `git bash` or `terminal`. If it matches, enter `yes` to succeed.
```shell
ssh -T git@github.com
```
 ## Pull Request Workflow
If you're not familiar with Pull Request, don't worry! The following guidance will tell you how to create a Pull Request step by step. If you want to dive into the development mode of Pull Request, you can refer to the [official documents](https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/about-pull-requests)
### 1. Fork and clone
If you are posting a pull request for the first time, you should fork the OpenMMLab repositories by clicking the **Fork** button in the top right corner of the GitHub page, and the forked repositories will appear under your GitHub profile.
## Pull Request Workflow
If you're not familiar with Pull Request, don't worry! The following guidance will tell you how to create a Pull Request step by step. If you want to dive into the development mode of Pull Request, you can refer to the [official documents](https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/about-pull-requests)
### 1. Fork and clone
If you are posting a pull request for the first time, you should fork the OpenMMLab repositories by clicking the **Fork** button in the top right corner of the GitHub page, and the forked repositories will appear under your GitHub profile.
 Then, you can clone the repositories to local:
```shell
git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git
```
After that, you should get into the project folder and add official repository as the upstream repository.
```bash
cd mmyolo
git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo
```
Check whether the remote repository has been added successfully by `git remote -v`
```bash
origin git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git (fetch)
origin git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git (push)
upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo (fetch)
upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo (push)
```
```{note}
Here's a brief introduction to the origin and upstream. When we use "git clone", we create an "origin" remote by default, which points to the repository cloned from. As for "upstream", we add it ourselves to point to the target repository. Of course, if you don't like the name "upstream", you could name it as you wish. Usually, we'll push the code to "origin". If the pushed code conflicts with the latest code in official("upstream"), we should pull the latest code from upstream to resolve the conflicts, and then push to "origin" again. The posted Pull Request will be updated automatically.
```
### 2. Configure pre-commit
You should configure [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) in the local development environment to make sure the code style matches that of OpenMMLab. **Note**: The following code should be executed under the MMYOLO directory.
```shell
pip install -U pre-commit
pre-commit install
```
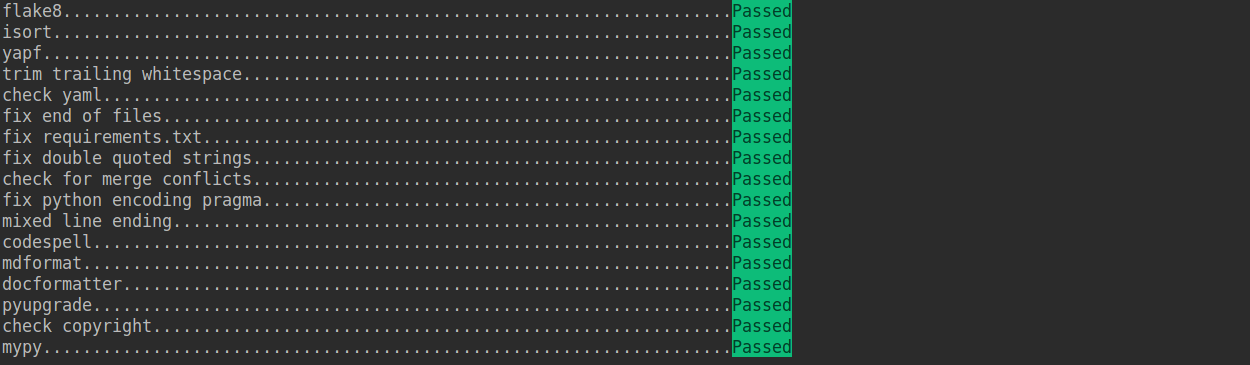
Check that pre-commit is configured successfully, and install the hooks defined in `.pre-commit-config.yaml`.
```shell
pre-commit run --all-files
```
Then, you can clone the repositories to local:
```shell
git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git
```
After that, you should get into the project folder and add official repository as the upstream repository.
```bash
cd mmyolo
git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo
```
Check whether the remote repository has been added successfully by `git remote -v`
```bash
origin git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git (fetch)
origin git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git (push)
upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo (fetch)
upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo (push)
```
```{note}
Here's a brief introduction to the origin and upstream. When we use "git clone", we create an "origin" remote by default, which points to the repository cloned from. As for "upstream", we add it ourselves to point to the target repository. Of course, if you don't like the name "upstream", you could name it as you wish. Usually, we'll push the code to "origin". If the pushed code conflicts with the latest code in official("upstream"), we should pull the latest code from upstream to resolve the conflicts, and then push to "origin" again. The posted Pull Request will be updated automatically.
```
### 2. Configure pre-commit
You should configure [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) in the local development environment to make sure the code style matches that of OpenMMLab. **Note**: The following code should be executed under the MMYOLO directory.
```shell
pip install -U pre-commit
pre-commit install
```
Check that pre-commit is configured successfully, and install the hooks defined in `.pre-commit-config.yaml`.
```shell
pre-commit run --all-files
```
 ```{note}
Chinese users may fail to download the pre-commit hooks due to the network issue. In this case, you could download these hooks from gitee by setting the .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
pre-commit install -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
pre-commit run --all-files -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
```
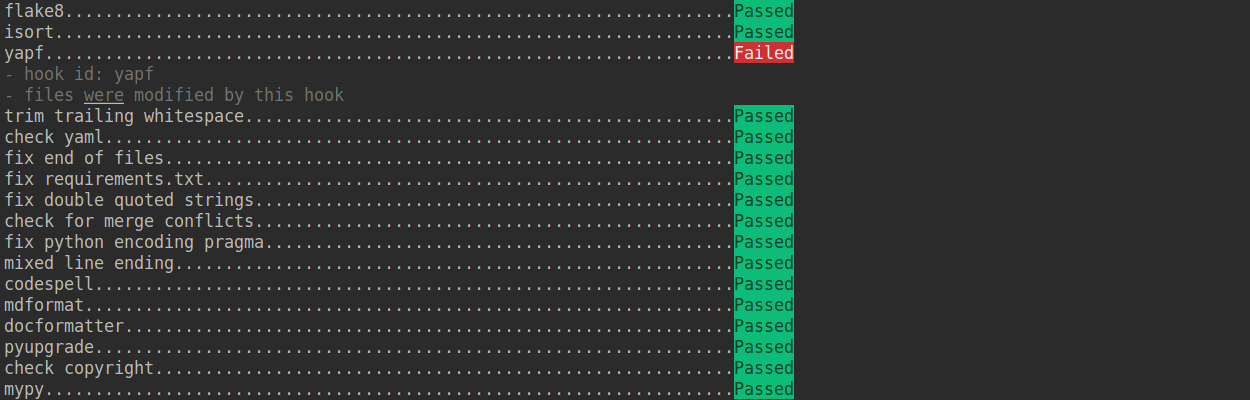
If the installation process is interrupted, you can repeatedly run `pre-commit run ... ` to continue the installation.
If the code does not conform to the code style specification, pre-commit will raise a warning and fixes some of the errors automatically.
```{note}
Chinese users may fail to download the pre-commit hooks due to the network issue. In this case, you could download these hooks from gitee by setting the .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
pre-commit install -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
pre-commit run --all-files -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
```
If the installation process is interrupted, you can repeatedly run `pre-commit run ... ` to continue the installation.
If the code does not conform to the code style specification, pre-commit will raise a warning and fixes some of the errors automatically.
 If we want to commit our code bypassing the pre-commit hook, we can use the `--no-verify` option(**only for temporarily commit**).
```shell
git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
```
### 3. Create a development branch
After configuring the pre-commit, we should create a branch based on the dev branch to develop the new feature or fix the bug. The proposed branch name is `username/pr_name`
```shell
git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
```
In subsequent development, if the dev branch of the local repository is behind the dev branch of "upstream", we need to pull the upstream for synchronization, and then execute the above command:
```shell
git pull upstream dev
```
### 4. Commit the code and pass the unit test
- MMYOLO introduces mypy to do static type checking to increase the robustness of the code. Therefore, we need to add Type Hints to our code and pass the mypy check. If you are not familiar with Type Hints, you can refer to [this tutorial](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
- The committed code should pass through the unit test
```shell
# Pass all unit tests
pytest tests
# Pass the unit test of yolov5_coco dataset
pytest tests/test_datasets/test_yolov5_coco.py
```
If the unit test fails for lack of dependencies, you can install the dependencies referring to the [guidance](#unit-test)
- If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result referring to [guidance](#document-rendering)
### 5. Push the code to remote
We could push the local commits to remote after passing through the check of unit test and pre-commit. You can associate the local branch with remote branch by adding `-u` option.
```shell
git push -u origin {branch_name}
```
This will allow you to use the `git push` command to push code directly next time, without having to specify a branch or the remote repository.
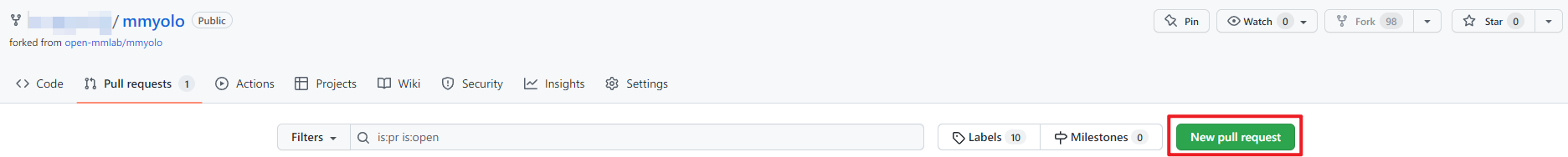
### 6. Create a Pull Request
(1) Create a pull request in GitHub's Pull request interface
If we want to commit our code bypassing the pre-commit hook, we can use the `--no-verify` option(**only for temporarily commit**).
```shell
git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
```
### 3. Create a development branch
After configuring the pre-commit, we should create a branch based on the dev branch to develop the new feature or fix the bug. The proposed branch name is `username/pr_name`
```shell
git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
```
In subsequent development, if the dev branch of the local repository is behind the dev branch of "upstream", we need to pull the upstream for synchronization, and then execute the above command:
```shell
git pull upstream dev
```
### 4. Commit the code and pass the unit test
- MMYOLO introduces mypy to do static type checking to increase the robustness of the code. Therefore, we need to add Type Hints to our code and pass the mypy check. If you are not familiar with Type Hints, you can refer to [this tutorial](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
- The committed code should pass through the unit test
```shell
# Pass all unit tests
pytest tests
# Pass the unit test of yolov5_coco dataset
pytest tests/test_datasets/test_yolov5_coco.py
```
If the unit test fails for lack of dependencies, you can install the dependencies referring to the [guidance](#unit-test)
- If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result referring to [guidance](#document-rendering)
### 5. Push the code to remote
We could push the local commits to remote after passing through the check of unit test and pre-commit. You can associate the local branch with remote branch by adding `-u` option.
```shell
git push -u origin {branch_name}
```
This will allow you to use the `git push` command to push code directly next time, without having to specify a branch or the remote repository.
### 6. Create a Pull Request
(1) Create a pull request in GitHub's Pull request interface
 (2) Modify the PR description according to the guidelines so that other developers can better understand your changes.
```{note}
The *base* branch should be modified to *dev* branch.
```
(2) Modify the PR description according to the guidelines so that other developers can better understand your changes.
```{note}
The *base* branch should be modified to *dev* branch.
```
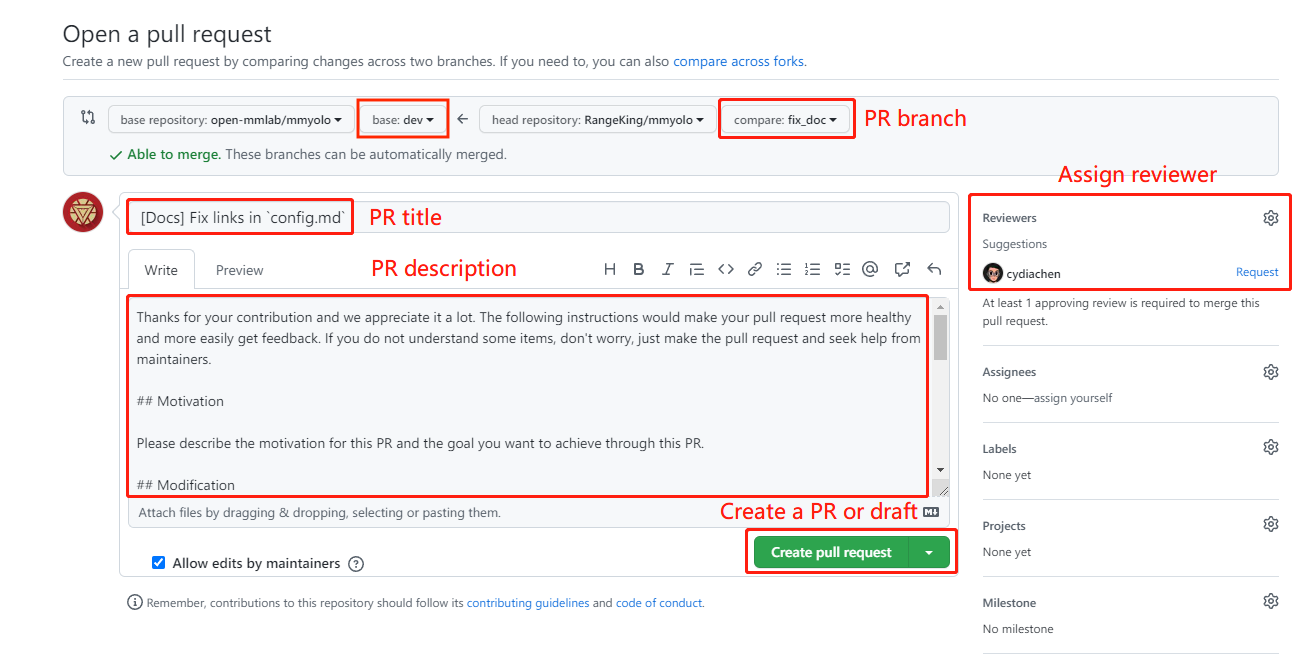 Find more details about Pull Request description in [pull request guidelines](#pr-specs).
**note**
(a) The Pull Request description should contain the reason for the change, the content of the change, and the impact of the change, and be associated with the relevant Issue (see [documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue))
(b) If it is your first contribution, please sign the CLA
Find more details about Pull Request description in [pull request guidelines](#pr-specs).
**note**
(a) The Pull Request description should contain the reason for the change, the content of the change, and the impact of the change, and be associated with the relevant Issue (see [documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue))
(b) If it is your first contribution, please sign the CLA
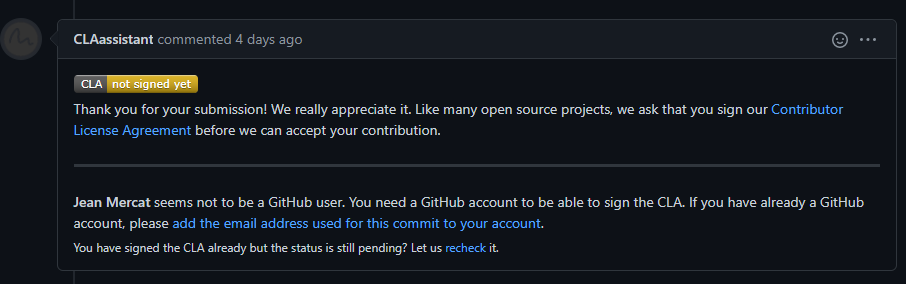 (c) Check whether the Pull Request pass through the CI
(c) Check whether the Pull Request pass through the CI
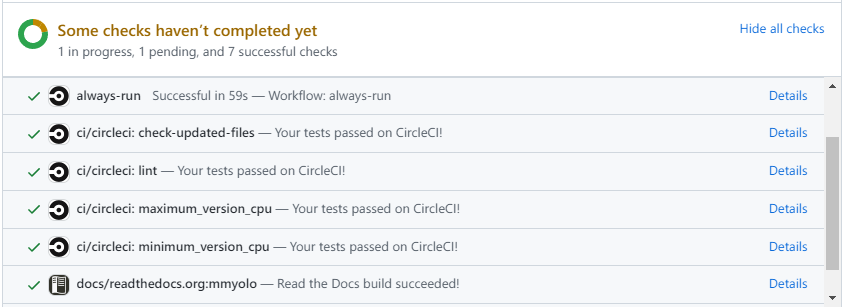 MMYOLO will run unit test for the posted Pull Request on Linux, based on different versions of Python, and PyTorch to make sure the code is correct. We can see the specific test information by clicking `Details` in the above image so that we can modify the code.
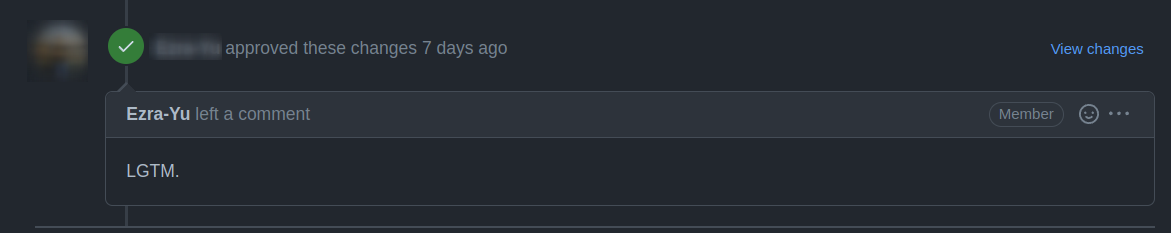
(3) If the Pull Request passes the CI, then you can wait for the review from other developers. You'll modify the code based on the reviewer's comments, and repeat the steps [4](#4-commit-the-code-and-pass-the-unit-test)-[5](#5-push-the-code-to-remote) until all reviewers approve it. Then, we will merge it ASAP.
MMYOLO will run unit test for the posted Pull Request on Linux, based on different versions of Python, and PyTorch to make sure the code is correct. We can see the specific test information by clicking `Details` in the above image so that we can modify the code.
(3) If the Pull Request passes the CI, then you can wait for the review from other developers. You'll modify the code based on the reviewer's comments, and repeat the steps [4](#4-commit-the-code-and-pass-the-unit-test)-[5](#5-push-the-code-to-remote) until all reviewers approve it. Then, we will merge it ASAP.
 ### 7. Resolve conflicts
If your local branch conflicts with the latest dev branch of "upstream", you'll need to resolove them. There are two ways to do this:
```shell
git fetch --all --prune
git rebase upstream/dev
```
or
```shell
git fetch --all --prune
git merge upstream/dev
```
If you are very good at handling conflicts, then you can use rebase to resolve conflicts, as this will keep your commit logs tidy. If you are unfamiliar with `rebase`, you can use `merge` to resolve conflicts.
## Guidance
### Unit test
We should also make sure the committed code will not decrease the coverage of unit test, we could run the following command to check the coverage of unit test:
```shell
python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
python -m coverage html
# check file in htmlcov/index.html
```
### Document rendering
If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result. We could install the dependencies and run the following command to render the documents and check the results:
```shell
pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
cd docs/zh_cn/
# or docs/en
make html
# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
```
## Code style
### Python
We adopt [PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) as the preferred code style.
We use the following tools for linting and formatting:
- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): A wrapper around some linter tools.
- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): A Python utility to sort imports.
- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): A formatter for Python files.
- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): A Python utility to fix common misspellings in text files.
- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): Mdformat is an opinionated Markdown formatter that can be used to enforce a consistent style in Markdown files.
- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): A formatter to format docstring.
Style configurations of yapf and isort can be found in [setup.cfg](../../../setup.cfg).
We use [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) that checks and formats for `flake8`, `yapf`, `isort`, `trailing whitespaces`, `markdown files`,
fixes `end-of-files`, `double-quoted-strings`, `python-encoding-pragma`, `mixed-line-ending`, sorts `requirments.txt` automatically on every commit.
The config for a pre-commit hook is stored in [.pre-commit-config](../../../.pre-commit-config.yaml).
### C++ and CUDA
We follow the [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html).
## PR Specs
1. Use [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com) hook to avoid issues of code style
2. One short-time branch should be matched with only one PR
3. Accomplish a detailed change in one PR. Avoid large PR
- Bad: Support Faster R-CNN
- Acceptable: Add a box head to Faster R-CNN
- Good: Add a parameter to box head to support custom conv-layer number
4. Provide clear and significant commit message
5. Provide clear and meaningful PR description
- Task name should be clarified in title. The general format is: \[Prefix\] Short description of the PR (Suffix)
- Prefix: add new feature \[Feature\], fix bug \[Fix\], related to documents \[Docs\], in developing \[WIP\] (which will not be reviewed temporarily)
- Introduce main changes, results and influences on other modules in short description
- Associate related issues and pull requests with a milestone
### 7. Resolve conflicts
If your local branch conflicts with the latest dev branch of "upstream", you'll need to resolove them. There are two ways to do this:
```shell
git fetch --all --prune
git rebase upstream/dev
```
or
```shell
git fetch --all --prune
git merge upstream/dev
```
If you are very good at handling conflicts, then you can use rebase to resolve conflicts, as this will keep your commit logs tidy. If you are unfamiliar with `rebase`, you can use `merge` to resolve conflicts.
## Guidance
### Unit test
We should also make sure the committed code will not decrease the coverage of unit test, we could run the following command to check the coverage of unit test:
```shell
python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
python -m coverage html
# check file in htmlcov/index.html
```
### Document rendering
If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result. We could install the dependencies and run the following command to render the documents and check the results:
```shell
pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
cd docs/zh_cn/
# or docs/en
make html
# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
```
## Code style
### Python
We adopt [PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) as the preferred code style.
We use the following tools for linting and formatting:
- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): A wrapper around some linter tools.
- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): A Python utility to sort imports.
- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): A formatter for Python files.
- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): A Python utility to fix common misspellings in text files.
- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): Mdformat is an opinionated Markdown formatter that can be used to enforce a consistent style in Markdown files.
- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): A formatter to format docstring.
Style configurations of yapf and isort can be found in [setup.cfg](../../../setup.cfg).
We use [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) that checks and formats for `flake8`, `yapf`, `isort`, `trailing whitespaces`, `markdown files`,
fixes `end-of-files`, `double-quoted-strings`, `python-encoding-pragma`, `mixed-line-ending`, sorts `requirments.txt` automatically on every commit.
The config for a pre-commit hook is stored in [.pre-commit-config](../../../.pre-commit-config.yaml).
### C++ and CUDA
We follow the [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html).
## PR Specs
1. Use [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com) hook to avoid issues of code style
2. One short-time branch should be matched with only one PR
3. Accomplish a detailed change in one PR. Avoid large PR
- Bad: Support Faster R-CNN
- Acceptable: Add a box head to Faster R-CNN
- Good: Add a parameter to box head to support custom conv-layer number
4. Provide clear and significant commit message
5. Provide clear and meaningful PR description
- Task name should be clarified in title. The general format is: \[Prefix\] Short description of the PR (Suffix)
- Prefix: add new feature \[Feature\], fix bug \[Fix\], related to documents \[Docs\], in developing \[WIP\] (which will not be reviewed temporarily)
- Introduce main changes, results and influences on other modules in short description
- Associate related issues and pull requests with a milestone
 Click `New SSH key` to add a new SSH keys, and paste the copied content into Key.
Click `New SSH key` to add a new SSH keys, and paste the copied content into Key.
 Finally, verify that SSH matches the GitHub account by running the command in `git bash` or `terminal`. If it matches, enter `yes` to succeed.
```shell
ssh -T git@github.com
```
Finally, verify that SSH matches the GitHub account by running the command in `git bash` or `terminal`. If it matches, enter `yes` to succeed.
```shell
ssh -T git@github.com
```
 ## Pull Request Workflow
If you're not familiar with Pull Request, don't worry! The following guidance will tell you how to create a Pull Request step by step. If you want to dive into the development mode of Pull Request, you can refer to the [official documents](https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/about-pull-requests)
### 1. Fork and clone
If you are posting a pull request for the first time, you should fork the OpenMMLab repositories by clicking the **Fork** button in the top right corner of the GitHub page, and the forked repositories will appear under your GitHub profile.
## Pull Request Workflow
If you're not familiar with Pull Request, don't worry! The following guidance will tell you how to create a Pull Request step by step. If you want to dive into the development mode of Pull Request, you can refer to the [official documents](https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/about-pull-requests)
### 1. Fork and clone
If you are posting a pull request for the first time, you should fork the OpenMMLab repositories by clicking the **Fork** button in the top right corner of the GitHub page, and the forked repositories will appear under your GitHub profile.
 Then, you can clone the repositories to local:
```shell
git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git
```
After that, you should get into the project folder and add official repository as the upstream repository.
```bash
cd mmyolo
git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo
```
Check whether the remote repository has been added successfully by `git remote -v`
```bash
origin git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git (fetch)
origin git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git (push)
upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo (fetch)
upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo (push)
```
```{note}
Here's a brief introduction to the origin and upstream. When we use "git clone", we create an "origin" remote by default, which points to the repository cloned from. As for "upstream", we add it ourselves to point to the target repository. Of course, if you don't like the name "upstream", you could name it as you wish. Usually, we'll push the code to "origin". If the pushed code conflicts with the latest code in official("upstream"), we should pull the latest code from upstream to resolve the conflicts, and then push to "origin" again. The posted Pull Request will be updated automatically.
```
### 2. Configure pre-commit
You should configure [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) in the local development environment to make sure the code style matches that of OpenMMLab. **Note**: The following code should be executed under the MMYOLO directory.
```shell
pip install -U pre-commit
pre-commit install
```
Check that pre-commit is configured successfully, and install the hooks defined in `.pre-commit-config.yaml`.
```shell
pre-commit run --all-files
```
Then, you can clone the repositories to local:
```shell
git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git
```
After that, you should get into the project folder and add official repository as the upstream repository.
```bash
cd mmyolo
git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo
```
Check whether the remote repository has been added successfully by `git remote -v`
```bash
origin git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git (fetch)
origin git@github.com:{username}/mmyolo.git (push)
upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo (fetch)
upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmyolo (push)
```
```{note}
Here's a brief introduction to the origin and upstream. When we use "git clone", we create an "origin" remote by default, which points to the repository cloned from. As for "upstream", we add it ourselves to point to the target repository. Of course, if you don't like the name "upstream", you could name it as you wish. Usually, we'll push the code to "origin". If the pushed code conflicts with the latest code in official("upstream"), we should pull the latest code from upstream to resolve the conflicts, and then push to "origin" again. The posted Pull Request will be updated automatically.
```
### 2. Configure pre-commit
You should configure [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) in the local development environment to make sure the code style matches that of OpenMMLab. **Note**: The following code should be executed under the MMYOLO directory.
```shell
pip install -U pre-commit
pre-commit install
```
Check that pre-commit is configured successfully, and install the hooks defined in `.pre-commit-config.yaml`.
```shell
pre-commit run --all-files
```

 ```{note}
Chinese users may fail to download the pre-commit hooks due to the network issue. In this case, you could download these hooks from gitee by setting the .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
pre-commit install -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
pre-commit run --all-files -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
```
If the installation process is interrupted, you can repeatedly run `pre-commit run ... ` to continue the installation.
If the code does not conform to the code style specification, pre-commit will raise a warning and fixes some of the errors automatically.
```{note}
Chinese users may fail to download the pre-commit hooks due to the network issue. In this case, you could download these hooks from gitee by setting the .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
pre-commit install -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
pre-commit run --all-files -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
```
If the installation process is interrupted, you can repeatedly run `pre-commit run ... ` to continue the installation.
If the code does not conform to the code style specification, pre-commit will raise a warning and fixes some of the errors automatically.
 If we want to commit our code bypassing the pre-commit hook, we can use the `--no-verify` option(**only for temporarily commit**).
```shell
git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
```
### 3. Create a development branch
After configuring the pre-commit, we should create a branch based on the dev branch to develop the new feature or fix the bug. The proposed branch name is `username/pr_name`
```shell
git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
```
In subsequent development, if the dev branch of the local repository is behind the dev branch of "upstream", we need to pull the upstream for synchronization, and then execute the above command:
```shell
git pull upstream dev
```
### 4. Commit the code and pass the unit test
- MMYOLO introduces mypy to do static type checking to increase the robustness of the code. Therefore, we need to add Type Hints to our code and pass the mypy check. If you are not familiar with Type Hints, you can refer to [this tutorial](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
- The committed code should pass through the unit test
```shell
# Pass all unit tests
pytest tests
# Pass the unit test of yolov5_coco dataset
pytest tests/test_datasets/test_yolov5_coco.py
```
If the unit test fails for lack of dependencies, you can install the dependencies referring to the [guidance](#unit-test)
- If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result referring to [guidance](#document-rendering)
### 5. Push the code to remote
We could push the local commits to remote after passing through the check of unit test and pre-commit. You can associate the local branch with remote branch by adding `-u` option.
```shell
git push -u origin {branch_name}
```
This will allow you to use the `git push` command to push code directly next time, without having to specify a branch or the remote repository.
### 6. Create a Pull Request
(1) Create a pull request in GitHub's Pull request interface
If we want to commit our code bypassing the pre-commit hook, we can use the `--no-verify` option(**only for temporarily commit**).
```shell
git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
```
### 3. Create a development branch
After configuring the pre-commit, we should create a branch based on the dev branch to develop the new feature or fix the bug. The proposed branch name is `username/pr_name`
```shell
git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
```
In subsequent development, if the dev branch of the local repository is behind the dev branch of "upstream", we need to pull the upstream for synchronization, and then execute the above command:
```shell
git pull upstream dev
```
### 4. Commit the code and pass the unit test
- MMYOLO introduces mypy to do static type checking to increase the robustness of the code. Therefore, we need to add Type Hints to our code and pass the mypy check. If you are not familiar with Type Hints, you can refer to [this tutorial](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
- The committed code should pass through the unit test
```shell
# Pass all unit tests
pytest tests
# Pass the unit test of yolov5_coco dataset
pytest tests/test_datasets/test_yolov5_coco.py
```
If the unit test fails for lack of dependencies, you can install the dependencies referring to the [guidance](#unit-test)
- If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result referring to [guidance](#document-rendering)
### 5. Push the code to remote
We could push the local commits to remote after passing through the check of unit test and pre-commit. You can associate the local branch with remote branch by adding `-u` option.
```shell
git push -u origin {branch_name}
```
This will allow you to use the `git push` command to push code directly next time, without having to specify a branch or the remote repository.
### 6. Create a Pull Request
(1) Create a pull request in GitHub's Pull request interface
 (2) Modify the PR description according to the guidelines so that other developers can better understand your changes.
```{note}
The *base* branch should be modified to *dev* branch.
```
(2) Modify the PR description according to the guidelines so that other developers can better understand your changes.
```{note}
The *base* branch should be modified to *dev* branch.
```
 Find more details about Pull Request description in [pull request guidelines](#pr-specs).
**note**
(a) The Pull Request description should contain the reason for the change, the content of the change, and the impact of the change, and be associated with the relevant Issue (see [documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue))
(b) If it is your first contribution, please sign the CLA
Find more details about Pull Request description in [pull request guidelines](#pr-specs).
**note**
(a) The Pull Request description should contain the reason for the change, the content of the change, and the impact of the change, and be associated with the relevant Issue (see [documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue))
(b) If it is your first contribution, please sign the CLA
 (c) Check whether the Pull Request pass through the CI
(c) Check whether the Pull Request pass through the CI
 MMYOLO will run unit test for the posted Pull Request on Linux, based on different versions of Python, and PyTorch to make sure the code is correct. We can see the specific test information by clicking `Details` in the above image so that we can modify the code.
(3) If the Pull Request passes the CI, then you can wait for the review from other developers. You'll modify the code based on the reviewer's comments, and repeat the steps [4](#4-commit-the-code-and-pass-the-unit-test)-[5](#5-push-the-code-to-remote) until all reviewers approve it. Then, we will merge it ASAP.
MMYOLO will run unit test for the posted Pull Request on Linux, based on different versions of Python, and PyTorch to make sure the code is correct. We can see the specific test information by clicking `Details` in the above image so that we can modify the code.
(3) If the Pull Request passes the CI, then you can wait for the review from other developers. You'll modify the code based on the reviewer's comments, and repeat the steps [4](#4-commit-the-code-and-pass-the-unit-test)-[5](#5-push-the-code-to-remote) until all reviewers approve it. Then, we will merge it ASAP.
 ### 7. Resolve conflicts
If your local branch conflicts with the latest dev branch of "upstream", you'll need to resolove them. There are two ways to do this:
```shell
git fetch --all --prune
git rebase upstream/dev
```
or
```shell
git fetch --all --prune
git merge upstream/dev
```
If you are very good at handling conflicts, then you can use rebase to resolve conflicts, as this will keep your commit logs tidy. If you are unfamiliar with `rebase`, you can use `merge` to resolve conflicts.
## Guidance
### Unit test
We should also make sure the committed code will not decrease the coverage of unit test, we could run the following command to check the coverage of unit test:
```shell
python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
python -m coverage html
# check file in htmlcov/index.html
```
### Document rendering
If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result. We could install the dependencies and run the following command to render the documents and check the results:
```shell
pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
cd docs/zh_cn/
# or docs/en
make html
# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
```
## Code style
### Python
We adopt [PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) as the preferred code style.
We use the following tools for linting and formatting:
- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): A wrapper around some linter tools.
- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): A Python utility to sort imports.
- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): A formatter for Python files.
- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): A Python utility to fix common misspellings in text files.
- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): Mdformat is an opinionated Markdown formatter that can be used to enforce a consistent style in Markdown files.
- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): A formatter to format docstring.
Style configurations of yapf and isort can be found in [setup.cfg](../../../setup.cfg).
We use [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) that checks and formats for `flake8`, `yapf`, `isort`, `trailing whitespaces`, `markdown files`,
fixes `end-of-files`, `double-quoted-strings`, `python-encoding-pragma`, `mixed-line-ending`, sorts `requirments.txt` automatically on every commit.
The config for a pre-commit hook is stored in [.pre-commit-config](../../../.pre-commit-config.yaml).
### C++ and CUDA
We follow the [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html).
## PR Specs
1. Use [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com) hook to avoid issues of code style
2. One short-time branch should be matched with only one PR
3. Accomplish a detailed change in one PR. Avoid large PR
- Bad: Support Faster R-CNN
- Acceptable: Add a box head to Faster R-CNN
- Good: Add a parameter to box head to support custom conv-layer number
4. Provide clear and significant commit message
5. Provide clear and meaningful PR description
- Task name should be clarified in title. The general format is: \[Prefix\] Short description of the PR (Suffix)
- Prefix: add new feature \[Feature\], fix bug \[Fix\], related to documents \[Docs\], in developing \[WIP\] (which will not be reviewed temporarily)
- Introduce main changes, results and influences on other modules in short description
- Associate related issues and pull requests with a milestone
### 7. Resolve conflicts
If your local branch conflicts with the latest dev branch of "upstream", you'll need to resolove them. There are two ways to do this:
```shell
git fetch --all --prune
git rebase upstream/dev
```
or
```shell
git fetch --all --prune
git merge upstream/dev
```
If you are very good at handling conflicts, then you can use rebase to resolve conflicts, as this will keep your commit logs tidy. If you are unfamiliar with `rebase`, you can use `merge` to resolve conflicts.
## Guidance
### Unit test
We should also make sure the committed code will not decrease the coverage of unit test, we could run the following command to check the coverage of unit test:
```shell
python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
python -m coverage html
# check file in htmlcov/index.html
```
### Document rendering
If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result. We could install the dependencies and run the following command to render the documents and check the results:
```shell
pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
cd docs/zh_cn/
# or docs/en
make html
# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
```
## Code style
### Python
We adopt [PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) as the preferred code style.
We use the following tools for linting and formatting:
- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): A wrapper around some linter tools.
- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): A Python utility to sort imports.
- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): A formatter for Python files.
- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): A Python utility to fix common misspellings in text files.
- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): Mdformat is an opinionated Markdown formatter that can be used to enforce a consistent style in Markdown files.
- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): A formatter to format docstring.
Style configurations of yapf and isort can be found in [setup.cfg](../../../setup.cfg).
We use [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) that checks and formats for `flake8`, `yapf`, `isort`, `trailing whitespaces`, `markdown files`,
fixes `end-of-files`, `double-quoted-strings`, `python-encoding-pragma`, `mixed-line-ending`, sorts `requirments.txt` automatically on every commit.
The config for a pre-commit hook is stored in [.pre-commit-config](../../../.pre-commit-config.yaml).
### C++ and CUDA
We follow the [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html).
## PR Specs
1. Use [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com) hook to avoid issues of code style
2. One short-time branch should be matched with only one PR
3. Accomplish a detailed change in one PR. Avoid large PR
- Bad: Support Faster R-CNN
- Acceptable: Add a box head to Faster R-CNN
- Good: Add a parameter to box head to support custom conv-layer number
4. Provide clear and significant commit message
5. Provide clear and meaningful PR description
- Task name should be clarified in title. The general format is: \[Prefix\] Short description of the PR (Suffix)
- Prefix: add new feature \[Feature\], fix bug \[Fix\], related to documents \[Docs\], in developing \[WIP\] (which will not be reviewed temporarily)
- Introduce main changes, results and influences on other modules in short description
- Associate related issues and pull requests with a milestone